
Cell Division.
The process by which a cell divides to form two daughter cells. Upon completion of the process, each daughter cell contains the same genetic material as the original cell and roughly half of its cytoplasm. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/cell%20division
Cell Division Video:
Either of the two strands formed when a chromosome duplicates itself as part of the early stages of cell division. The chromatids are joined together by a single centromere and later separate to become individual chromosomes. ttp://dictionary.reference.com/browse/chromatid
a specialized structure on the chromosome, appearing during cell division as the constricted central region where the two chromatids are held together and form an X shape. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/centromere

Interphase.
The stage in the development of a cell following mitosis or meiosis, during which the nucleus is not dividing. In cells that will undergo further division, the DNA in the nucleus is duplicated in preparation for the next division. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/interphase
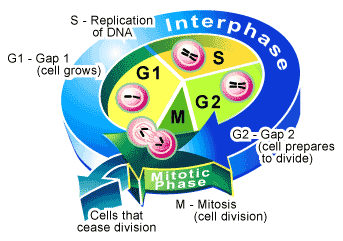
Cell Cycle.
The series of events involving the growth, replication, and division of a eukaryotic cell. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/cell%20cycle
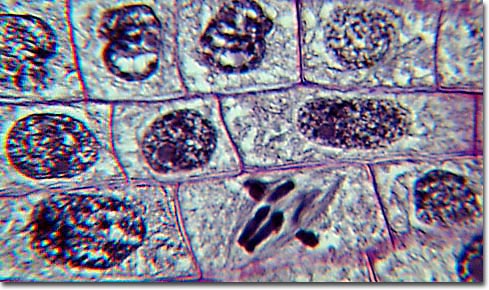
Mitosis.
The process in cell division by which the nucleus divides, typically consisting of four stages, and normally resulting in two new nuclei, each of which contains a complete copy of the parental chromosomes. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/mitosis
The first stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes condense and become visible, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the spindle apparatus forms at opposite poles of the cell. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/prophase


Centriole.
One of a pair of small cylindrical cell organelles near the nucleus in animal cells; composed of nine triplet microtubules and form the asters during mitosis http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/centriole
Spindle.
A spindle-shaped structure, composed of microtubules, that forms near the cell nucleus during mitosis or meiosis and, as it divides, draws the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/spindle


Metaphase.
The stage of mitosis and meiosis, following prophase and preceding anaphase, during which the chromosomes are aligned along the metaphase plate. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/metaphase
Anaphase.
The stage of cell division in mitosis or meiosis in which the doubled set of chromosomes separates into two identical groups that move to opposite ends of the cell. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/anaphase


Telophase.
the final stage of meiosis or mitosis, in which the separated chromosomes reach the opposite poles of the dividing cell and the nuclei of the daughter cells form around the two sets of chromosomes. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/telophase
Cytokinesis.
The division of the cytoplasm of a cell following the division of the nucleus. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/cytokinesis


Cyclin.
A class of proteins that fluctuate in concentration at specific points during the cell cycle and that regulate the cycle by binding to a kinase. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/cyclin
Cancer.
a malignant and invasive growth or tumor, esp. one originating in epithelium, tending to recur after excision and to metastasize to other sites. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/cancer






No comments:
Post a Comment